As you migrate your IT infrastructure to Amazon Web Services (AWS), and your data transitions from traditional on-premises data centers to the AWS infrastructure, it’s imperative that you understand — as an IT manager — the burden you carry for protecting your organization’s data. More importantly, it’s critical that you do not fall subject to the misconception that your AWS workloads are protected simply because they are hosted on the AWS infrastructure.
To eliminate this misconception and distinguish what each party is responsible for, AWS deployed the AWS shared responsibility model. This model defines a separation of powers — what AWS is responsible for and what its customers are responsible for when it comes to data security and compliance. Let’s dive further into the AWS shared responsibility model and why a third-party data protection solution like Druva is critical for protecting and managing your organization’s essential data.
What is the AWS shared responsibility model?
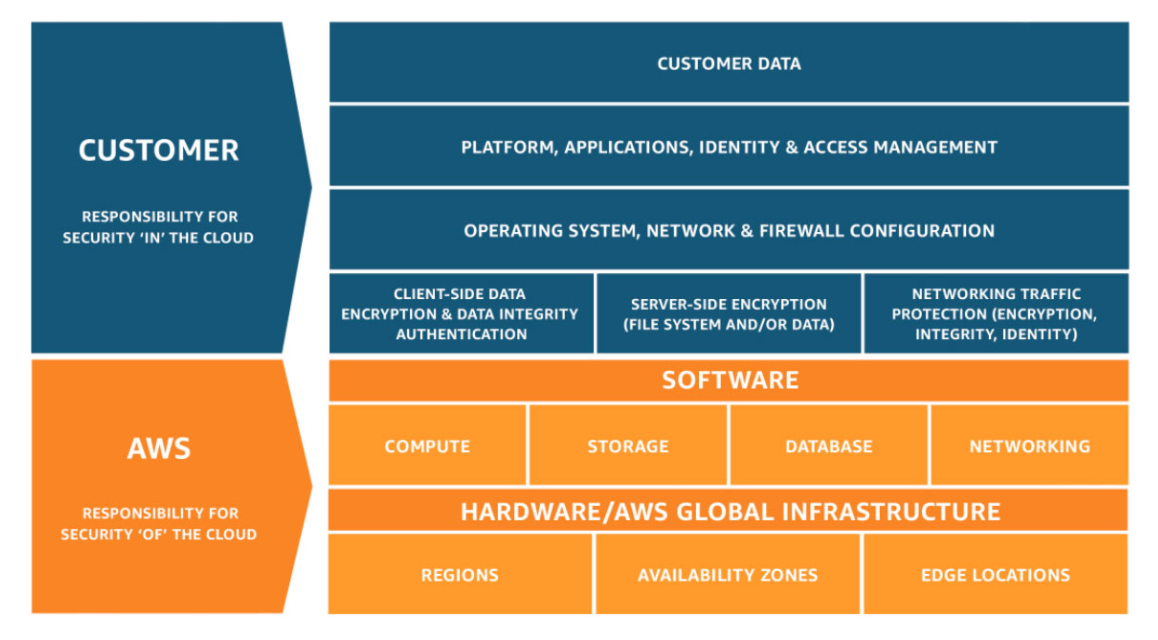
The AWS shared responsibility model is a shared model that establishes the operational partnership between the customer and AWS. Under the shared responsibility model, AWS provides the infrastructure burden — “security of the cloud” — while customers are responsible for and must protect their data in their AWS cloud workloads — “security in the cloud.”
“Security of the cloud” in the AWS shared responsibility model
As part of the AWS shared responsibility model, AWS states that it is responsible for the “security of the cloud.” This means that AWS is responsible for the cloud infrastructure which includes: hardware, software, networking, and the physical protection of the facilities that run AWS Cloud services.
What are AWS customers responsible for in the shared responsibility model?
In the AWS shared responsibility model, customer responsibility is for the “security in the cloud.” As a customer, the headache of managing and protecting the infrastructure is no longer an issue — AWS takes care of that responsibility. However, the onus is on the customer to protect and back up all customer data, the platform, operating systems, applications, and providing or restricting all access management to its users.
While AWS seeks to lessen the customer burden by providing the “security of the cloud,” the customer burden varies depending on “levels of abstraction.“ As AWS launched its infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), customers became responsible for security depending on their level of abstraction. Depending on the level of customer abstraction, there is a corresponding version of the AWS shared responsibility model1:
- AWS shared responsibility model for EC2
- AWS shared responsibility model for containers
- AWS shared responsibility model for Lambda
To further illustrate the shared controls within the AWS shared responsibility model, some examples include2:
- Patch management: AWS is responsible for patching and fixing flaws within the infrastructure, but customers are responsible for patching their guest OS and applications.
- Configuration management: AWS maintains the configuration of its infrastructure devices, but a customer is responsible for configuring their own guest operating systems, databases, and applications.
- Awareness and training: AWS trains AWS employees, but a customer must train their own employees.