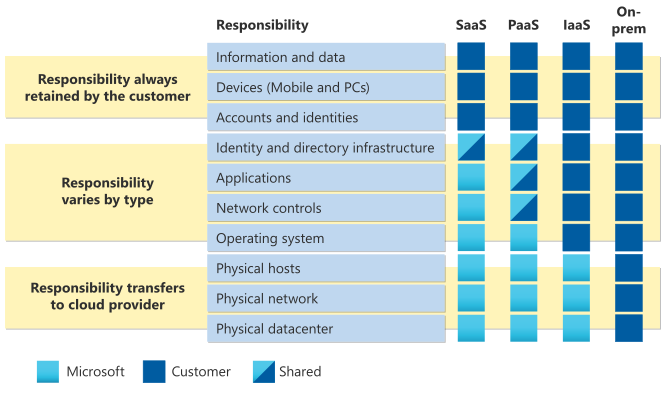
Relying on Legal Hold as a backup is like relying on your email archive to recover lost project files—it wasn’t built for that purpose. For true operational resilience, organizations must invest in purpose-built backup solutions that allow them to restore exactly what they need, when they need it, without legal intervention or compliance overhead.
Myth 3: Data Retention Policies Protect Data After User Deletion
A common misconception is that Microsoft’s retention policies protect user data after deletion. In reality, when a Microsoft 365 user is removed, all associated data — emails, OneDrive files, and Teams chats — are permanently deleted after a short grace period, unless specific retention policies are pre-configured in the Microsoft Purview Compliance Center. Even then, data is only kept temporarily and isn’t easily restorable. In large enterprises, it’s especially challenging to ensure that data is correctly mapped to the right retention policies — and that those policies are properly configured, consistently applied, and regularly maintained.
Microsoft 365 Default Retention Periods:
- Exchange Online: 30 days for deleted mailboxes; 14–30 days for recoverable items.
- Microsoft Teams: 30 days for deleted conversations; channel conversations are stored in Exchange Online.
- SharePoint Online: 93 days in the Recycle Bin
- Planner: 30 days for deleted tasks and plans.
- OneDrive: 30 days for deleted content (extendable to 93 days).
- Entra ID: 30 days for deleted users and groups.
These are lifecycle extensions, not backups. Unlike true backups, there are no point-in-time snapshots or granular recovery option, making recovery impossible after the retention window expires.
Myth 4: Ransomware Protection is Built-In and Comprehensive
Microsoft 365 provides baseline ransomware detection and some recovery options, but these measures are far from comprehensive. Sophisticated ransomware attacks can easily circumvent these basic protections, especially when targeting compromised credentials or exploiting internal access controls.
Where Microsoft's Protection Falls Short:
- Delayed Detection: Anomaly-based detection may not catch ransomware early, allowing encryption damage to spread.
- Limited Recovery: OneDrive and SharePoint offer versioning and recycle bin recovery, but these are inadequate for large-scale attacks.
- Credential Vulnerabilities: If admin credentials are compromised, ransomware can disable protections and alter configurations undetected.
- User Dependence: Recovery often relies on manual file restoration, which is neither automated nor instant.
For true ransomware resilience, third-party solutions are needed for immutable, air-gapped backups with granular recovery.
Myth 5: Internal Threats Are Rare and Easily Managed
It's a common belief that data loss and breaches are primarily caused by external cyber threats. However, insider threats — both malicious and accidental — account for a significant portion of data loss incidents. These can include anything from accidental deletions by employees to deliberate data theft by rogue admins.
Where Microsoft's Built-in Protection Falls Short:
- Limited Visibility: Microsoft 365 provides basic audit logs, but tracking internal activity across Exchange, SharePoint, Teams, and OneDrive is often fragmented and lacks real-time visibility. This makes it difficult to spot suspicious behaviors early.
- Inadequate Access Controls: Native role-based access configurations can be bypassed or improperly set, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive data without clear traceability.
- No Granular Restore: If a malicious insider permanently deletes or corrupts files, recovery through native tools is limited to broad, less-targeted restores, risking the loss of recent changes.
To effectively combat insider threats, organizations require enhanced monitoring, granular recovery options, and more robust auditing that extend beyond Microsoft's standard capabilities.
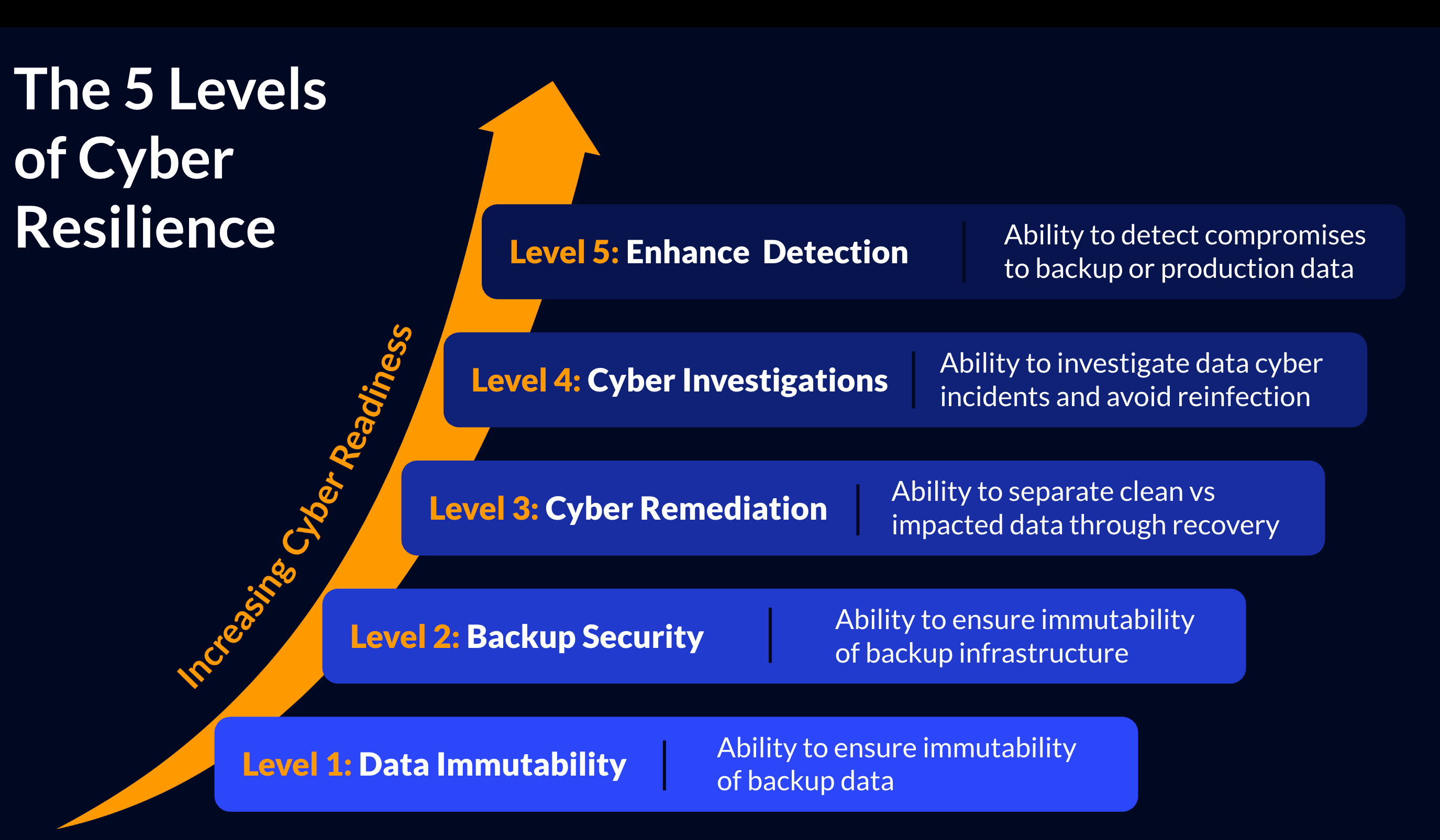
Why Multi-Layered Cyber Resilience is Non-Negotiable
Data vulnerabilities are escalating with the rise of sophisticated cyber threats:
- In 2024, ransomware attacks increased by 64%, with 55% targeting cloud-based applications.
- 60% of companies that suffer a major data loss shut down within six months (source: National Cyber Security Alliance).
- A report by Cybersecurity Ventures predicts global ransomware damages to hit $265 billion by 2031, with an attack every 2 seconds.
These alarming statistics highlight the urgency for enterprises to protect their Microsoft 365 data with robust, multi-layered cyber resilience strategies that involve deploying several protective measures across different layers — backup, infrastructure, recovery, compliance, and monitoring. To combat Microsoft 365 vulnerabilities, enterprises need to extend their protection beyond what Microsoft offers, ensuring backup, recoverability, and stringent monitoring at every layer.